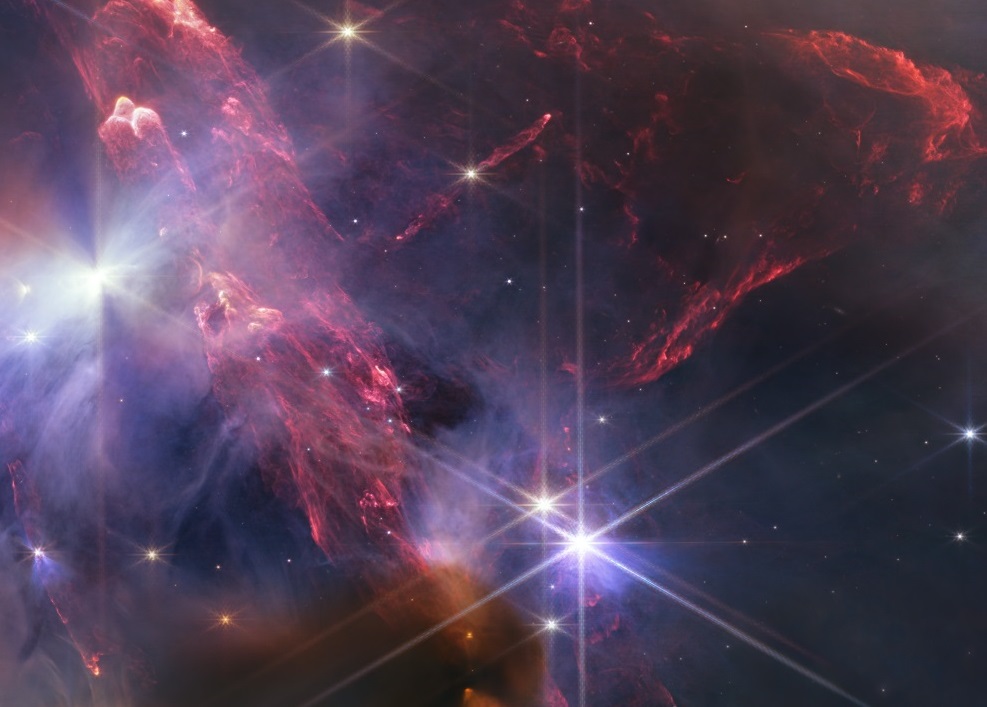
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope caps a successful first year of science, and stunning imagery, with a detailed view of the closest star-forming reg
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope caps a successful first year of science, and stunning imagery, with a detailed view of the closest star-forming region to Earth, the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, resulting in a dynamic image that belies the region’s relative quiet, and practically begs for explanation of what exactly we are looking at, reports NASA.
While dual jets have been seen blasting out of new stars before, the texture that Webb’s NIRCam instrument reveals in the multiple jets crisscrossing the image is unprecedented.

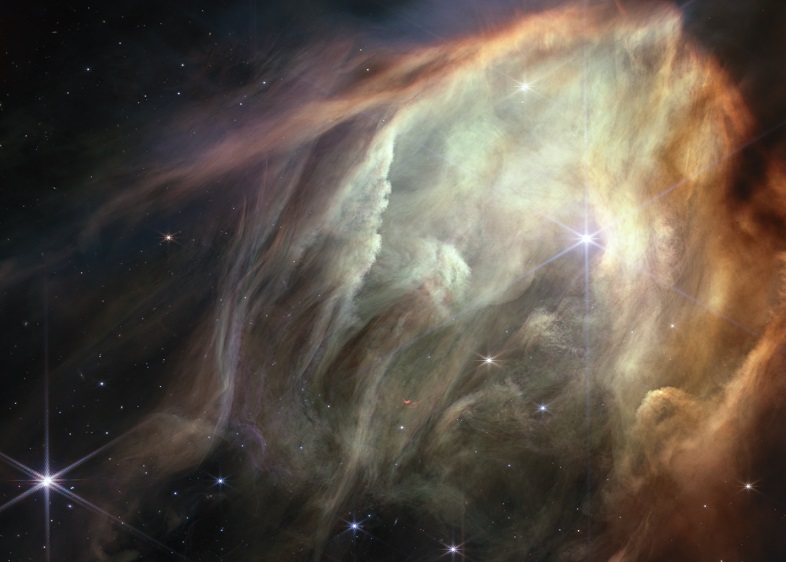
In striking contrast, the lower half of the image is dominated by a glowing cave of dust being lit up and eroded by the most massive star in the scene. Its stellar neighbors are the mass of our Sun or smaller, with some displaying the telltale shadows of protoplanetary disks, meaning we are looking at planetary systems potentially similar to our own in their earliest stages, reported NASA.
The first anniversary image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope displays star birth like it’s never been seen before, full of detailed, impressionistic texture. The subject is the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, the closest star-forming region to Earth.
It is a relatively small, quiet stellar nursery, but you’d never know it from Webb’s chaotic close-up. Jets bursting from young stars crisscross the image, impacting the surrounding interstellar gas and lighting up molecular hydrogen, shown in red, reported NASA.

From our cosmic backyard in the solar system to distant galaxies near the dawn of time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has delivered on its promise of revealing the universe like never before in its first year of science operations.
“In just one year, the James Webb Space Telescope has transformed humanity’s view of the cosmos, peering into dust clouds and seeing light from faraway corners of the universe for the very first time. Every new image is a new discovery, empowering scientists around the globe to ask and answer questions they once could never dream of,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
“Webb is an investment in American innovation but also a scientific feat made possible with NASA’s international partners that share a can-do spirit to push the boundaries of what is known to be possible. Thousands of engineers, scientists, and leaders poured their life’s passion into this mission, and their efforts will continue to improve our understanding of the origins of the universe – and our place in it”, said Nelson.
The new Webb image of Rho Ophiuchi features the nearest star-forming region to us. Its proximity at 390 light-years allows for a highly detailed close-up, with no foreground stars in the intervening space, reports NASA.

“On its first anniversary, the James Webb Space Telescope has already delivered upon its promise to unfold the universe, gifting humanity with a breathtaking treasure trove of images and science that will last for decades,” said Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
“An engineering marvel built by the world’s leading scientists and engineers, Webb has given us a more intricate understanding of galaxies, stars, and the atmospheres of planets outside of our solar system than ever before, laying the groundwork for NASA to lead the world in a new era of scientific discovery and the search for habitable worlds”, said Fox.
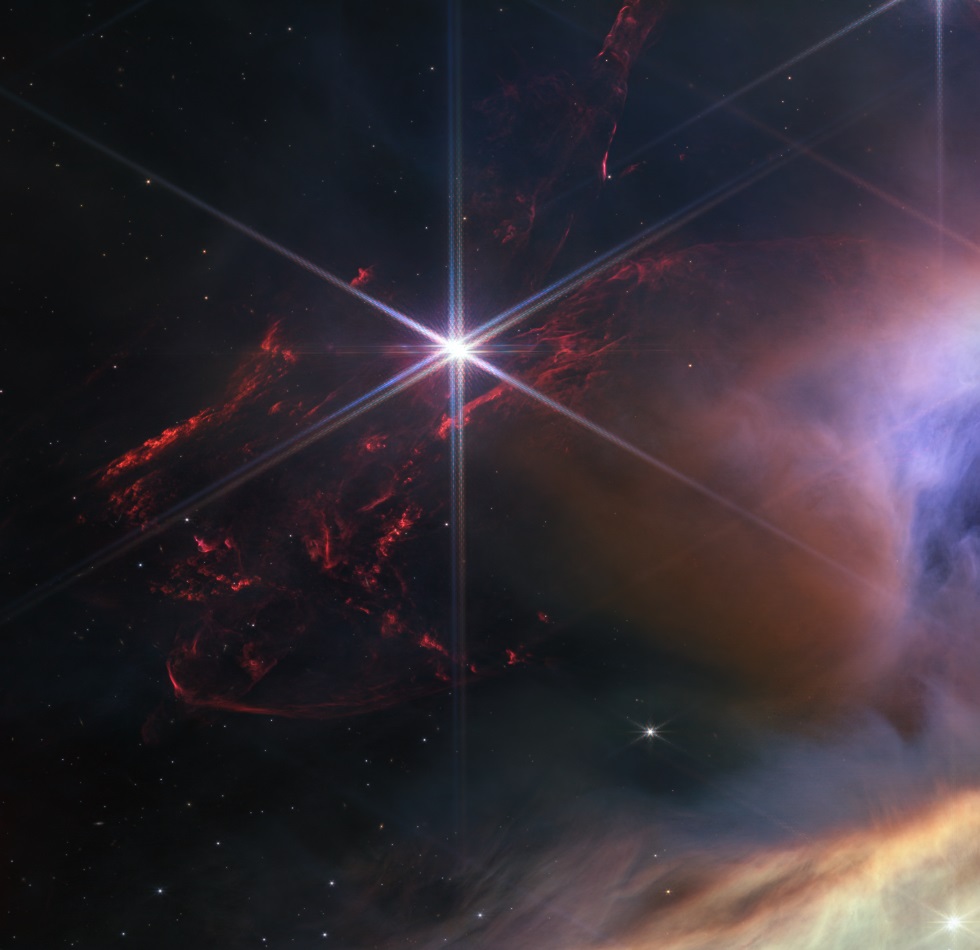

Webb’s image shows a region containing approximately 50 young stars, all of them similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The darkest areas are the densest, where thick dust cocoons still-forming protostars. Huge bipolar jets of molecular hydrogen, represented in red, dominate the image, appearing horizontally across the upper third and vertically on the right. These occur when a star first bursts through its natal envelope of cosmic dust, shooting out a pair of opposing jets into space like a newborn first stretching her arms out into the world. In contrast, the star S1 has carved out a glowing cave of dust in the lower half of the image. It is the only star in the image that is significantly more massive than the Sun, reported NASA.

“Webb’s image of Rho Ophiuchi allows us to witness a very brief period in the stellar lifecycle with new clarity. Our own Sun experienced a phase like this, long ago, and now we have the technology to see the beginning of another star’s story,” said Klaus Pontoppidan, who served as Webb project scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, since before the telescope’s launch and through the first year of operations.
Some stars in the image display tell-tale shadows indicating protoplanetary disks – potential future planetary systems in the making. Discover more details in the image video tour, or explore yourself in the zoomable image.
All Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI)


